

In the era of digital transformation, the business process landscape is not the only aspect undergoing significant changes; the darker side of life is also experiencing a digital metamorphosis. The vast digital interconnectivity driving global business processes has become a promising target for cybercriminals. Cybersecurity incidents affecting organizations and companies are often caused by vulnerabilities in their IT infrastructure and systems.
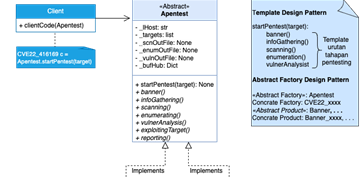
To address these vulnerabilities, organizations must continually update and evaluate their security posture. Strengthening this posture is only possible when vulnerabilities in the system are identified. The process of discovering these security vulnerabilities can be achieved through a security testing method known as penetration testing (Pentesting) or ethical hacking. However, the challenge lies in the fact that the pentesting process is time-consuming and involves several stages, including information gathering, network scanning, enumeration, vulnerability research, exploitation, and reporting. This complexity often requires the involvement of cybersecurity experts.
Given these challenges, automated approaches to penetration testing have emerged as a viable solution. These solutions come in the form of software frameworks designed to automate the penetration testing process. The pentesting methodology is based on specific exploitation of Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE), which has proven effective. The software framework being developed implements a design pattern that provides flexibility in enriching pentesting modules based on CVE.
Research conducted at the Network Technology and Applications Laboratory of the Department of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, Vocational College, UGM, aims to simplify the penetration testing process, making it accessible even to those without extensive cybersecurity expertise. By automating the pentesting process, organizations can significantly reduce the time and costs associated with hiring professional pentesters. This innovation aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly in improving ICT infrastructure and promoting sustainable industrialization.
The framework’s design allows for the easy integration of new modules, ensuring that it remains up-to-date with the latest CVEs. This adaptability is crucial in the rapidly evolving digital landscape, where new vulnerabilities constantly emerge. Additionally, an automated system can provide organizations with timely insights into their security posture, enabling them to address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
As the project progresses, the team at Vocational College, UGM, continues to work closely with industry partners to ensure that this autopentesting framework meets real-world needs. This collaboration not only enhances its relevance but also provides valuable insights into the challenges organizations face in maintaining robust cybersecurity measures.
In conclusion, the development of a CVE-based autopentesting framework represents a significant step forward in the field of cybersecurity. By leveraging automation, organizations can improve their security posture, reduce costs, and ultimately contribute to a safer digital environment. As we move further into the digital era, innovations like this will be essential in combating the ever-evolving threats posed by cybercriminals.

